What is SDLC?
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process or steps used by the software industry to design, develop and test high-quality software. The SDLC aims to produce high-quality software that meets or exceeds customer expectations and reaches completion within times and cost estimates.
SDLC consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, replace, and alter or enhance specific software. The life cycle defines a methodology for improving the quality of software and the overall development process.
To Simplify:

SDLC Phases
Below are the 8 main phases of the SDLC process.
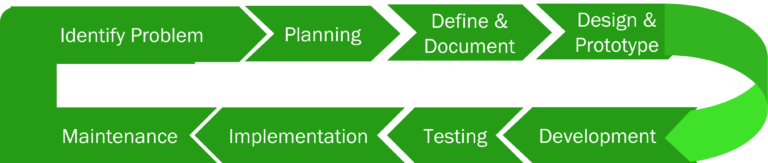
Phase 1: Identify the Problem
Problem Identification consists of:
- Clearly identifying the root cause of a problem.
- Developing a detailed problem statement that includes the problem’s effect on an organization’s health.
Many stakeholders are involved in the process. Stakeholders are people or groups closely affected by or concerned with the problem and are interested in policy solutions for it. Talking to stakeholders about the problem will help you with:
- Identifying the true, underlying problem
- Framing the problem accurately
Problems are unique to their contexts, so you will probably have to talk with several different stakeholders to get the full picture.
Phase 2: Planning
Planning means “thinking the Plan each and everything before the action takes place” about the Project goals, labor and material costs, timetable with goals, purpose, Scope, and every piece of information.
Planning for the quality assurance requirements and identification of the risks associated with the project is also done in the planning stage.
Some of the Example topics will be discussed in this planning phase:
- Develop Objectives
- Develop Tasks to Meet Objectives
- Determine Needed Resources
- Risk Assessment
- Cost and Human Resources
- Create a Timeline
- Determine Tracking and Assessment
- Finalize the plan
- Distribute the plan
Phase 3: Define and Document
Once the requirement analysis is done the next step is to clearly define and document the product requirements and get them approved by the customer or the market analysts. This is done through an SRS (Software Requirement Specification) document which consists of all the product requirements to be designed and developed during the project life cycle.
A piece of written, printed, drawn, presented, or Kept representation of thought about the application, that provides information or evidence or that serves as an official record.

Phase 4: Designing and Product Architecture
Design is a process to transform user requirements into some suitable form, which helps the programmer in software coding and implementation.
SRS is the reference for product architects to come out with the best architecture for the product to be developed. Based on the requirements specified in SRS, more than one design approach for the product architecture is usually proposed and documented in a DDS – Design Document Specification.
Phase 5: Development
The SDLC’s actual development starts and the product is built. The programming code is generated as per DDS(Design Document Specification) during this stage. If the design is detailed and organized, code generation can be accomplished without much hassle.
Developers must follow the coding guidelines defined by their organization and programming tools like compilers, interpreters, debuggers, etc. are used to generate the code.
Different high-level programming languages such as C, C++, Pascal, Java, and PHP are used for coding. The programming language is chosen with respect to the type of software being developed.
Phase 6: Testing
Software Testing is a method to check whether the actual software product matches expected requirements and to ensure that the software product is Defect free or not.
The purpose of software testing is to identify errors, gaps, or missing requirements in contrast to actual requirements. where product defects are reported, tracked, fixed, and retested until the product reaches the quality standards defined in the SRS.
The different types of tests are:
- Manual vs Automated testing
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- Functional tests
- End-to-end tests
- Acceptance testing
- Performance testing
- Smoke testing
Phase 7: Implementation
Software implementation is the process of adopting and integrating a software application into your company’s systems and workflows. This step of the process can be manual or automated, depending on the complexity and needs of the application.
The product may first be released in a limited segment and tested in the real business environment (UAT- User acceptance testing).
Phase 8: Maintenance
IT operations and maintenance, or IT O&M, is the process of monitoring, upgrading, and maintaining an organization’s applications and IT infrastructure on a continuous basis. IT O&M is critical in keeping IT systems and networks secure and operating effectively and efficiently.
SDLC Methodologies
The following are the most important and popular SDLC models followed in the industry:
- Agile
- Big-Bang
- DevOps
- Iterative
- Spiral
- V-Model
- Waterfall
SDLC Benefits
- SDLC provides an upfront, centralized goal for everyone to agree with and understand
- There is a clear plan for development
- Including resources and associated costs
- Roles can be assigned to ensure proper execution of the plan
References:
- https://www.servicenow.com/
- LinkedIn Community
- ITIL